In a world consumed by scarcity, the concept of non rivalrous goods offers a glimmer of hope. When we think of goods, we typically associate them with rivalries and competition. However, non rivalrous goods challenge the traditional ideas of consumption as we know it.
Table of Contents
Understanding Non Rivalrous Goods
Non rivalrous goods, also known as non rival goods or public goods, are resources that can be consumed by multiple individuals simultaneously without depleting or diminishing their availability. Unlike rivalrous goods, which are subject to scarcity and competition, non rivalrous goods have the potential to be shared and enjoyed by an unlimited number of users.
Examples of non rivalrous goods include public parks, street lights, knowledge, and digital content such as software, e-books, and streaming services. These goods can be accessed and utilized by multiple individuals without any negative impact on others’ ability to do the same.

Credit: www.amazon.com
The Rise of Non Rivalrous Goods in the Digital Economy
The digital revolution has played a significant role in the emergence and proliferation of non rivalrous goods. In the past, physical goods were often subject to scarcity and exclusivity. However, the rise of the internet and digital technologies has allowed for the creation and distribution of non rivalrous goods on a previously unimaginable scale.
One of the key characteristics of non rivalrous goods in the digital economy is their ability to be easily copied and shared without any additional cost or loss of quality. For example, once a piece of software is developed, it can be replicated infinitely and distributed to users all around the world, without diminishing the original copy or preventing others from enjoying the same software simultaneously.
This unique characteristic of non rivalrous goods has paved the way for the sharing economy, where individuals can share and access goods and services at a fraction of the cost. Platforms such as Uber, Airbnb, and Spotify exemplify the power of non rivalrous goods in transforming the way we consume and interact with resources.
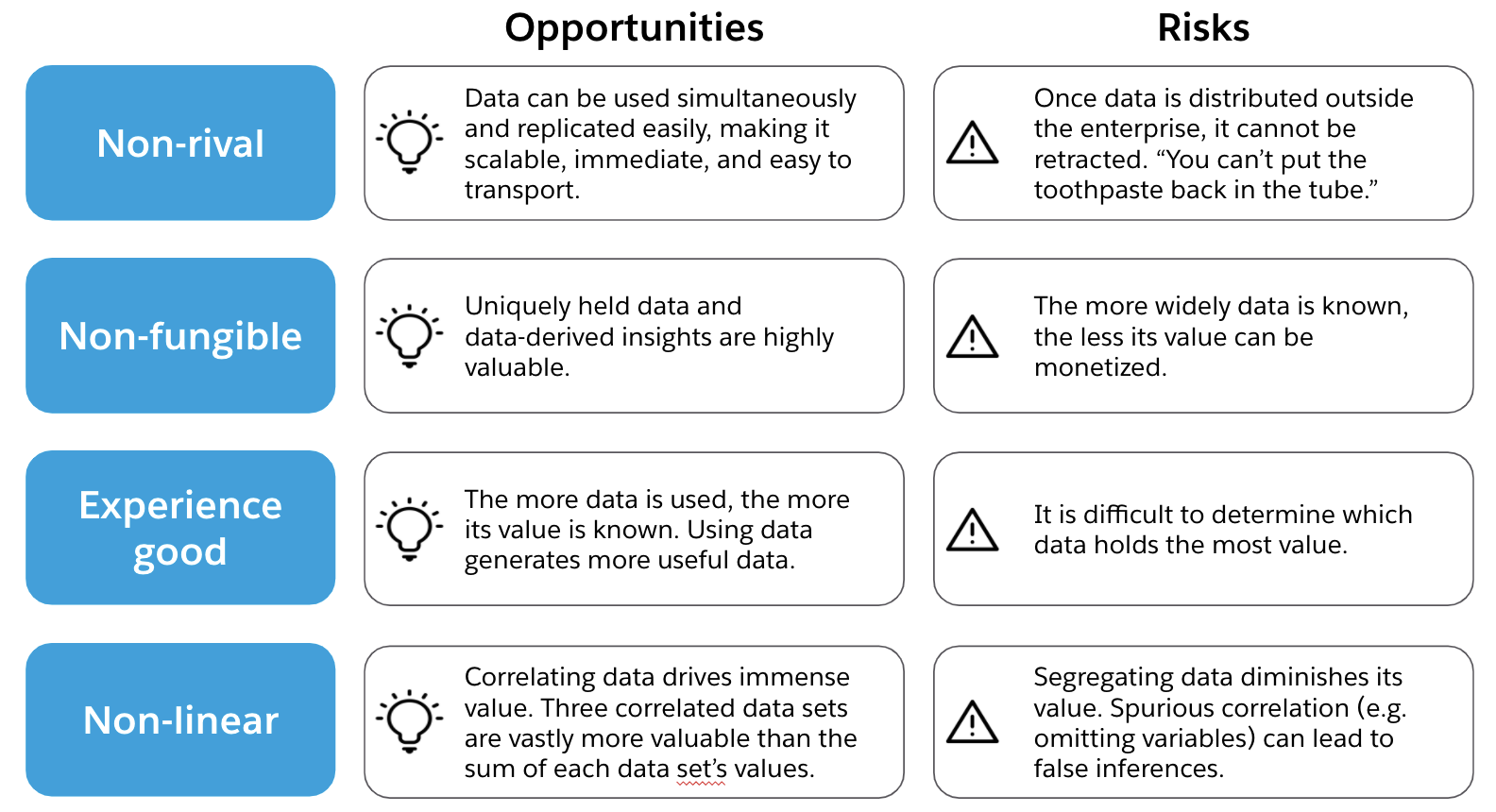
Credit: blogs.mulesoft.com
The Benefits of Non Rivalrous Goods
The concept of non rivalrous goods carries several benefits that contribute to its role as the future of consumption:
- Increased Efficiency: Non rivalrous goods promote efficient resource allocation, as they can be utilized by an unlimited number of users. This reduces the need for duplicate production and wasteful consumption.
- Cost Savings: Non rivalrous goods often come at a lower cost or can be accessed for free, allowing individuals to save money and allocate their resources to other areas.
- Knowledge Sharing: Non rivalrous goods, particularly in the form of knowledge and information, can be freely shared, leading to increased innovation, intellectual growth, and overall societal progress.
- Collaboration and Community Building: Non rivalrous goods encourage collaboration and cooperative consumption, fostering a sense of community among individuals who share common interests or needs.
The Challenges and Future Implications
While non rivalrous goods present a promising vision for the future of consumption, they are not without their challenges. The digital landscape raises concerns surrounding intellectual property rights, privacy, and security. Additionally, traditional economic models built upon rivalrous goods face disruption, potentially leading to social and economic upheaval.
Looking ahead, it will be crucial to find ways to balance the benefits of non rivalrous goods with the protection of individual rights and the maintenance of economic stability. As technology continues to advance and the digital economy evolves, society will need to adapt and create new frameworks to harness the full potential of non rivalrous goods.
Conclusion
The concept of non rivalrous goods challenges the traditional notions of scarcity and competition that have long governed consumption. As the digital economy thrives, non rivalrous goods are shaping the future of consumption by promoting efficiency, cost savings, knowledge sharing, and collaboration. While there are challenges to address, the potential for a more inclusive, sustainable, and community-driven economy makes non rivalrous goods an exciting frontier to explore.