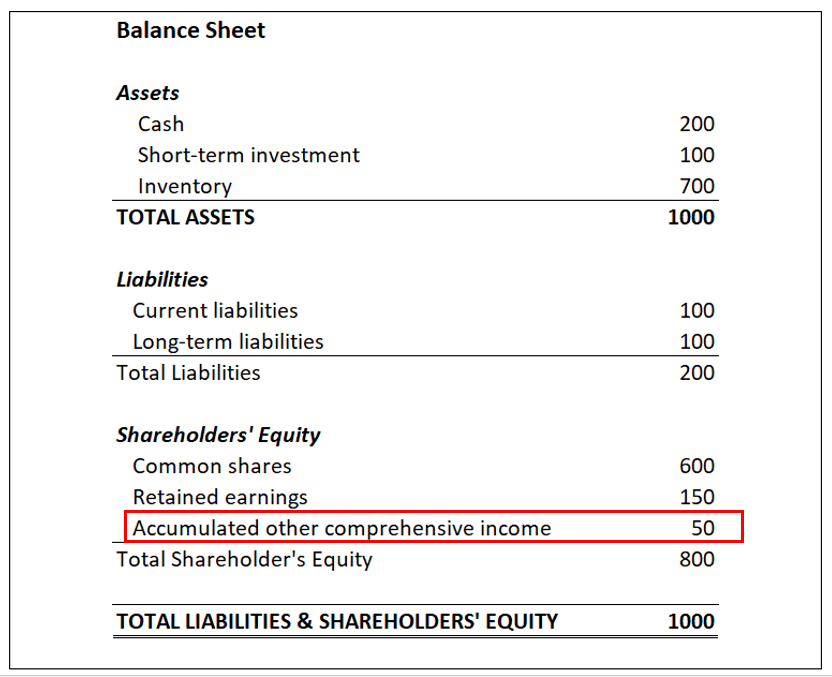
Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) is a category in financial reporting that represents gains and losses that are not included in net income but are instead recognized directly in equity. OCI is usually found in the statement of comprehensive income and is important for understanding the overall financial performance of a company.
OCI includes items that are not part of normal business operations and are therefore excluded from net income. These items are typically highlighted separately to provide a clear distinction between income and non-income related gains and losses.
Table of Contents
Examples of OCI items
There are several examples of OCI items that can affect a company’s financial statements. Some common examples include:
| OCI Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments | Fluctuations in exchange rates that impact the translation of foreign currency financial statements into the reporting currency. |
| Unrealized Gains/Losses on Available-for-Sale Securities | Gains or losses on investments that are classified as available-for-sale but have not yet been sold. |
| Actuarial Gains/Losses on Defined Benefit Pension Plans | Changes in the value of pension plans resulting from actuarial assumptions such as interest rates, life expectancies, or employee turnover. |
| Gains/Losses on Derivative Instruments | Changes in the fair value of derivative instruments used to hedge against specific risks. |
| Revaluation Surplus on Property, Plant, and Equipment | Increases or decreases in the value of fixed assets due to revaluation. |
These examples illustrate the variety of items that can impact OCI. It is important for investors and stakeholders to understand these items as they can provide valuable insights into a company’s financial health.
Credit: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Why is OCI important?
OCI helps in presenting a more comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance. By separating these items from net income, users of financial statements can better understand the underlying factors affecting a company’s profitability.
Additionally, OCI can impact other financial metrics as well. For example, OCI items are often included in calculations such as comprehensive income, which captures both net income and OCI. Comprehensive income provides a broader measure of a company’s financial performance.
Investors and analysts also consider OCI when evaluating a company’s financial stability and risk profile. Fluctuations in OCI items can reveal vulnerabilities and potential future risks that may not be immediately evident from net income alone.
Reporting and disclosure requirements
Financial reporting standards require companies to disclose OCI items in their financial statements. These items are typically presented in a separate statement or as a separate section within the statement of comprehensive income.
Companies are also required to provide detailed information about each OCI item, including the nature of the item, its impact on equity, and any related tax implications.
Transparency and clarity in reporting OCI items are essential for users of financial statements to make informed decisions. These disclosures enable investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to assess a company’s financial position and evaluate its future prospects.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Conclusion
Other Comprehensive Income is an important aspect of financial reporting that captures gains and losses not included in net income. These items provide additional insights into a company’s financial performance, stability, and risk profile. Understanding OCI and its impact on a company’s financial statements is crucial for investors and stakeholders to make informed decisions and evaluations. Financial reporting standards ensure proper disclosure and transparency regarding OCI, allowing users of financial statements to fully grasp a company’s financial health.
